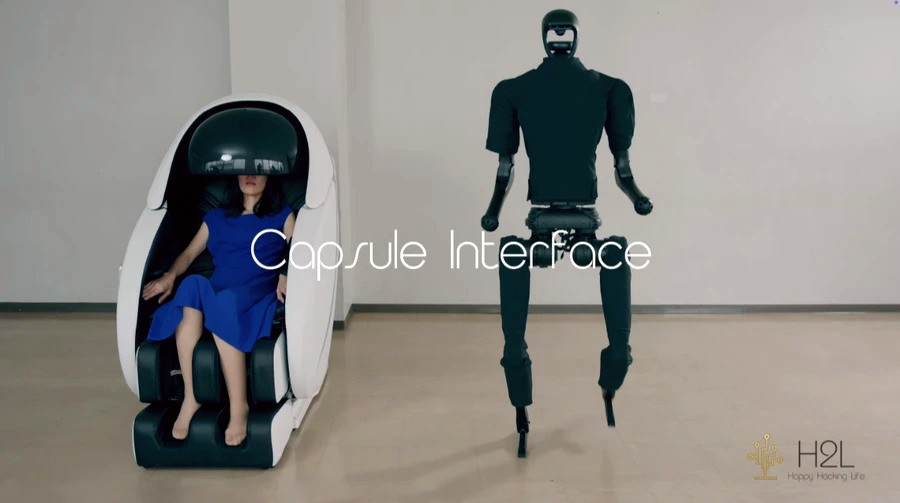
The Japanese company H2L has developed an innovative technology called Capsule Interface, which allows users to control humanoid robots through body movements and muscle strength. This system promises to enhance the precision and realism of remote robot control, as reported by Interesting Engineering.
The technology integrates sensors and software to detect even the slightest changes in the user's muscle tension. As a result, the robot not only replicates movements but also perceives the force applied by the operator. For instance, when a person lifts a heavy object, the robot 'understands' how much effort is required and replicates those sensations.
Conventional remote robotics relies on motion sensors or video systems, transmitting only limb positioning without conveying physical strain. In contrast, H2L's Capsule Interface utilizes muscle sensors to capture every impulse, adding realism to the control and ensuring a deeper immersion.
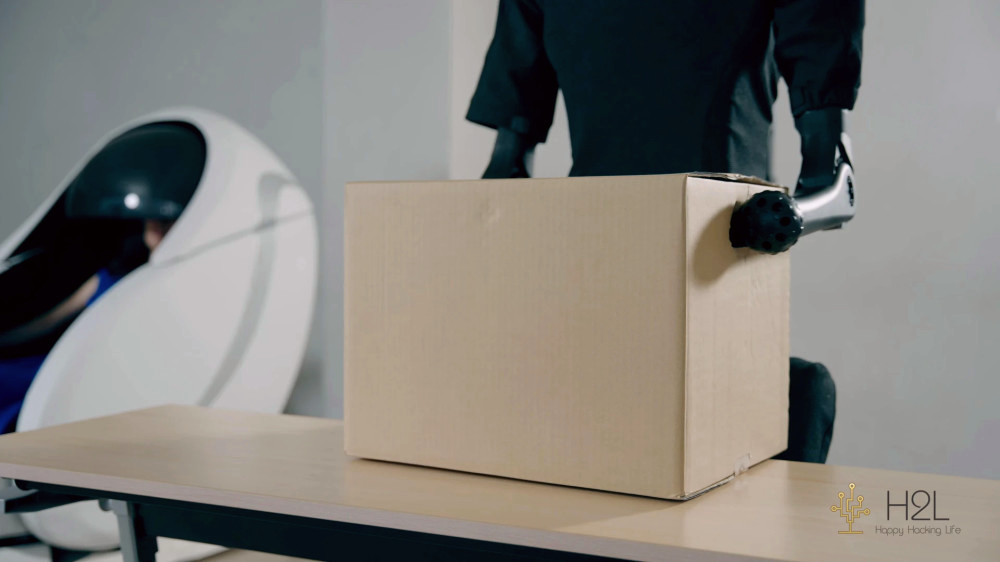
In a demonstration video, a woman operates the humanoid robot Unitree Robotics H1 using this system. The robot performs tasks such as moving objects and even interacting with another person—all thanks to the precise transmission of movements and efforts.
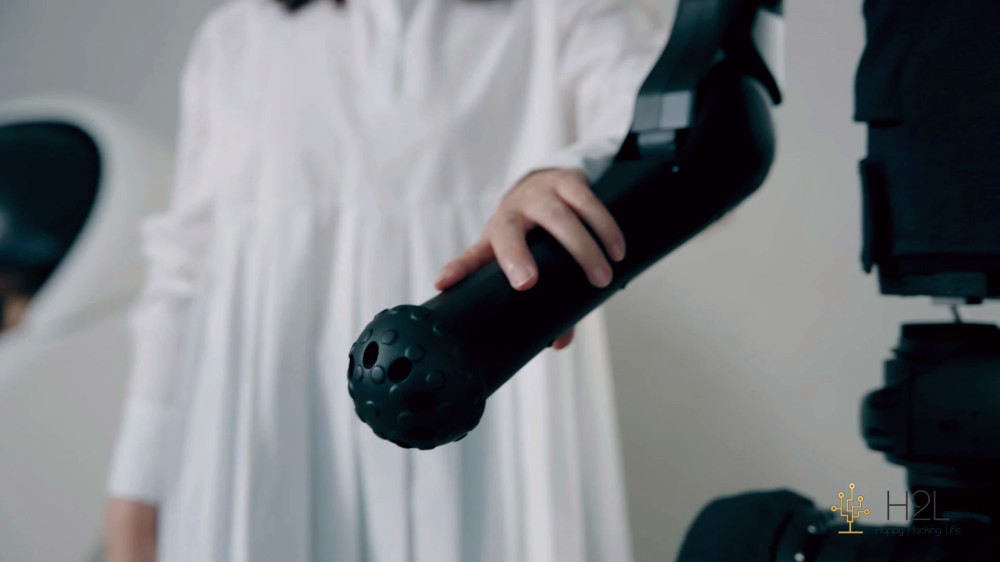
The Capsule Interface device is compact and can be used even while sitting or lying down. Unlike bulky systems, H2L's development is user-friendly and does not require extensive training. It includes muscle sensors, a display, and speakers for feedback, allowing users to simply settle into a comfortable chair or bed and start controlling.
This technology holds vast potential applications. It could be beneficial in industries and logistics—enabling workers to remotely move loads without physical strain or safely operate machinery in hazardous conditions. In daily life, it could assist the elderly or those with physical limitations, enabling them to cook, clean, or manage their homes from a distance.
Looking ahead, H2L plans to incorporate proprioceptive feedback into the device, allowing users to feel their body position and movements in space more acutely. Thus, Capsule Interface paves the way for a deeper interaction between humans and machines, adding emotional and physical realism even at a distance.